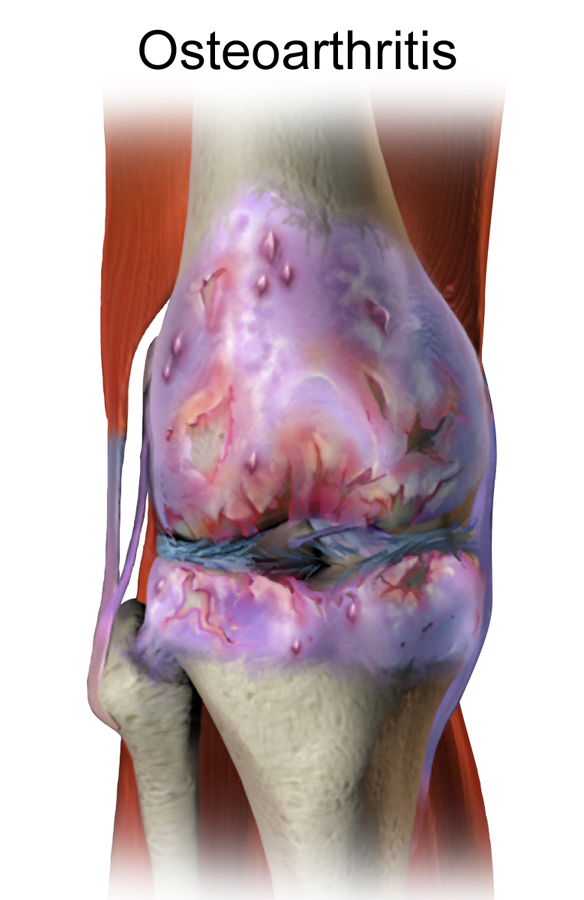
Osteoarthritis is a common and chronic joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in the joints wears down over time, causing pain, stiffness, swelling and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis can affect any joint, but it is most prevalent in the hands, knees, hips and spine. As any of us who suffer from it will attest, it is absolutely no fun at all.
Osteoarthritis is more common and severe in older adults, especially those over 50 years of age. There are several reasons why osteoarthritis affects seniors more than younger people, such as:
- Age-related changes in the cartilage, such as reduced water content, decreased ability to repair itself and increased susceptibility to damage.
- Cumulative wear and tear of the joints over the years, resulting from repetitive movements, injuries, surgeries or overuse.
- Increased prevalence of risk factors, such as obesity, that can contribute to the development and progression of osteoarthritis.
- Reduced muscle strength and bone density, which can affect the stability and support of the joints.
Because it can limit our daily activities and independence, osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on the quality of life and functional ability of seniors. Therefore, it is of critical importance to diagnose and treat osteoarthritis early and effectively.
There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but there are various treatments that can help relieve the symptoms, improve the joint function and slow down the disease progression. These are some of the main treatments health care providers recommend for their patients suffering from osteoarthritis:

By Bruce Blaus – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0,
https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=44968165
- Lifestyle measures, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, avoiding joint stress and using assistive devices. These can help reduce the pain and inflammation, strengthen the muscles and bones, increase the flexibility and mobility, and prevent further joint damage.
- Medications, such as pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs and antidepressants. These can help manage the pain and improve one’s mood, but they may have side effects and interactions with other drugs. Therefore, they should be used with caution and under medical supervision.
By Bruce Blaus – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0,
https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4496816
- Supportive therapies, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy and acupuncture. These can help provide education, guidance, exercises, massage, heat, cold and other modalities to enhance the joint function and reduce the pain.
- Surgical procedures, such as joint repair, joint replacement or joint fusion. These can help restore the joint structure and function, but they are invasive, costly and may have complications and risks. Therefore, they are usually reserved for severe cases that do not respond to other treatment.
So there you have it. Osteoarthritis is a common and chronic joint disease that affects seniors more than younger people. It can cause pain, stiffness, swelling and reduced mobility, which can affect the quality of life and functional ability of seniors. However, there are various treatments that can help relieve the symptoms, improve the joint function and slow down the disease progression. If you have any questions or concerns about osteoarthritis, please consult your doctor or health care provider.
By Steven Roberts

